Interactive Voice Response (IVR) is a technology that allows businesses to interact with customers through the use of voice and touch-tone inputs. It is typically used for telephone-based customer service, but can also be used for other purposes such as telemarketing, surveys, and appointment scheduling.
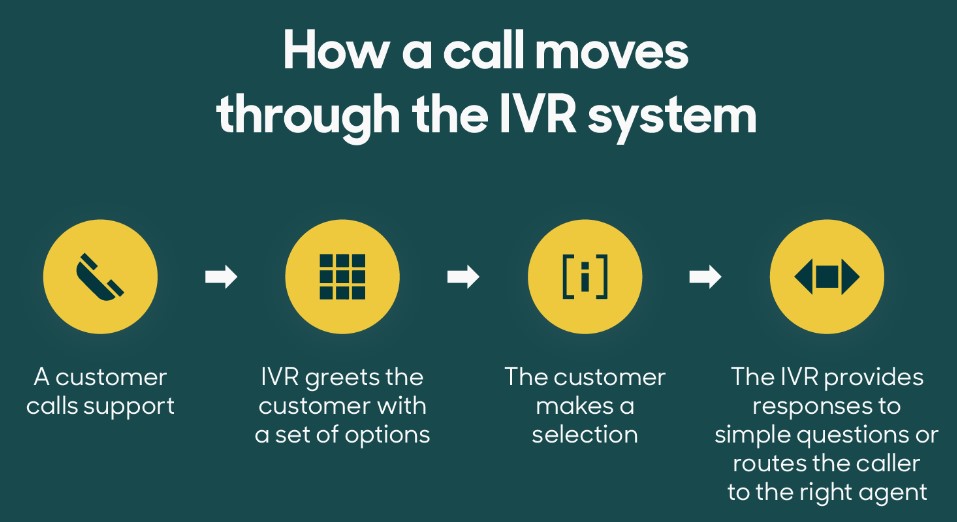
Inbound and outbound IVR systems use pre-recorded or computer-generated audio prompts to guide customers through a series of menu options. For example, a customer may be prompted to press a certain number to reach a specific department or to speak to their account number to verify their identity. The inbound and outbound IVR system then routes the call to the appropriate agent or department based on the customer’s input.
Inbound and outbound IVR technology can also be used for outbound calls, such as automated surveys or appointment reminders. It can also be integrated with other systems such as CRM and call center software to provide businesses with valuable data and insights into customer interactions.
Overall, inbound and outbound IVR systems can help businesses to improve customer service, increase efficiency, and reduce costs.
Inbound IVR
Explanation Of Inbound IVR And Its Uses
Inbound IVR (Interactive Voice Response) is a technology that allows a computer to interact with humans through the use of voice and DTMF (dual-tone multi-frequency) tones input via a keypad.
It’s commonly used in call centers to route calls to the appropriate agent or department, provide information to callers, and even handle simple transactions. IVR systems can also be used for customer service, allowing customers to check the status of an order, pay a bill, or report a problem.
Additionally, it can be used in lead generation, appointment scheduling, and other types of automated business processes. In summary, Inbound IVR is a technology that enables callers to interact with a computerized system, which can be used for a variety of purposes such as customer service, routing calls, and even simple transactions.
Benefits Of Inbound IVR For Businesses
There are several benefits of using inbound IVR for businesses, including:
- Improved Efficiency: Inbound IVR allows businesses to automate repetitive tasks, such as routing calls or providing information, which can free up employees to focus on more complex tasks.
- Increased Scalability: IVR systems can handle a large volume of calls simultaneously, which means businesses can handle more calls and serve more customers without needing to hire additional staff.
- Reduced Costs: By automating certain tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs associated with handling calls.
- Better Customer Service: IVR systems can provide customers with quick and accurate information, even outside of normal business hours. This can help improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved Data Collection: IVR systems can collect data on caller interactions, which can be used to improve business processes and gain insights into customer needs and preferences.
- Self-Service: IVR systems enable customers to handle simple tasks such as account balance inquiries, bill payments, and others without the need for human assistance.
- Multi-Language Support: IVR systems can be configured to support multiple languages, which can be beneficial for businesses serving customers in different regions or countries.
In summary, Inbound IVR can help businesses improve efficiency, increase scalability, reduce costs, improve customer service, and gain valuable insights into customer needs and preferences.
Outbound IVR
Explanation Of Outbound IVR And Its Uses
Outbound IVR (Interactive Voice Response) is a technology that allows a computer to initiate and conduct phone calls, play pre-recorded messages or collect information from the person answering the call. This can be used for a variety of purposes such as automated surveys, appointment reminders, political campaigns, and even telemarketing.
- Surveys: Outbound IVR systems can be used to conduct automated surveys, allowing businesses to gather customer feedback quickly and efficiently.
- Appointment Reminders: Outbound IVR can be used to remind customers of upcoming appointments, reducing the number of no-shows and increasing customer satisfaction.
- Marketing and Sales: Outbound IVR can be used for telemarketing and lead generation, allowing businesses to reach a large number of potential customers quickly and efficiently.
- Emergency notifications: Outbound IVR can be used to contact a large number of people simultaneously in case of emergency, providing them with important information and instructions.
- Political campaigns: Outbound IVR can be used to conduct automated political campaigns, allowing politicians to reach a large number of voters quickly and efficiently.
Outbound IVR can be a powerful tool for businesses and organizations looking to conduct automated phone campaigns, gather customer feedback, and much more. It can also help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of communication with customers and other stakeholders.
Benefits Of Outbound IVR For Businesses
There are several benefits of using outbound IVR for businesses, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Outbound IVR allows businesses to automate repetitive tasks, such as making calls or gathering information, which can free up employees to focus on more complex tasks.
- Increased Scalability: Outbound IVR systems can make a large volume of calls simultaneously, which means businesses can reach more customers without needing to hire additional staff.
- Reduced Costs: By automating certain tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs associated with making calls.
- Better Customer Service: Outbound IVR systems can provide customers with quick and accurate information, even outside of normal business hours. This can help improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved Data Collection: Outbound IVR systems can collect data on caller interactions, which can be used to improve business processes and gain insights into customer needs and preferences.
- Targeted Marketing: Outbound IVR systems can be configured to make calls to specific demographics, which can be beneficial for businesses looking to target specific market segments.
- Automated Follow-up: Outbound IVR can be used to follow up with customers automatically, reducing the need for human interaction and increasing the chances of conversion.
In summary, Outbound IVR can help businesses improve efficiency, increase scalability, reduce costs, improve customer service, and gain valuable insights into customer needs and preferences. It also allows for targeted marketing, automated follow-up, and better data collection.
Best Practices For Implementing IVR
Tips For Designing An Effective Inbound and Outbound IVR System
When designing an inbound and outbound IVR (Interactive Voice Response) system, it’s important to keep in mind the following tips to ensure that it is effective:
- Keep it simple: An IVR system should be easy to navigate, with a clear and simple menu structure. Avoid using technical jargon or complex language.
- Provide options: Offer multiple options for customers to choose from, such as language selection and department routing. This will make it easier for customers to reach the right person or the information they need.
- Personalize the experience: Use the customer’s name, account number, or other information to personalize the experience and make the customer feel valued.
- Test and measure: Test the IVR system with a small group of customers before rolling it out to the general public. Measure the success rate of the system, and make adjustments as needed.
- Provide a way to reach a human: Provide an option for customers to speak with a live agent if they are unable to find the information they need or if they are not satisfied with the automated system.
- Time-out: In case the customer didn’t respond to the IVR prompts, set a time-out mechanism to avoid long wait times and transfer the customer to an agent or a voicemail.
- Continuously improve: Continuously monitor the performance of the IVR system and gather feedback from customers and employees. Use this information to make improvements and enhance the customer experience.
- Keep the IVR up-to-date: Regularly update the IVR system with new information, such as changes in products or services, to ensure that customers always receive the most accurate information.
By following these tips, businesses can design an IVR system that is easy to navigate, efficient, and effective in meeting the needs of customers.
How To Measure The Success Of Your Inbound And Outbound IVR System
Measuring the success of an inbound and outbound IVR (Interactive Voice Response) system is crucial to ensure that it is meeting the needs of customers and achieving the desired business outcomes. Here are a few key metrics that can be used to measure the success of an IVR system:
- First Call Resolution (FCR): This measures the percentage of calls that are resolved without the need for transfer to a live agent. A high FCR indicates that the IVR system is effectively routing calls and providing accurate information to customers.
- Abandonment Rate: This measures the percentage of calls that are disconnected before the call is answered by an agent or the IVR system. A low abandonment rate indicates that customers are finding the IVR system easy to navigate and can reach the information or assistance they need.
- Average Handle Time (AHT): This measures the average time it takes for a customer to be connected to an agent or for the IVR system to provide the information the customer needs. A low AHT indicates that the IVR system is efficient and that customers are not experiencing long wait times.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): This measures the level of satisfaction customers have with the IVR system. It can be measured by conducting surveys or gathering feedback from customers. A high CSAT indicates that the IVR system is meeting the needs of customers and providing a positive experience.
- Call Volume: This measures the number of calls the IVR system is handling. A high call volume indicates that the IVR system is being heavily used and is meeting the needs of customers.
- Self-Service Success Rate: This measures the percentage of customers that can complete the task they called for using the IVR system.
By monitoring these metrics, businesses can gain insights into the performance of their IVR system and make adjustments as needed to improve the customer experience and achieve desired business outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inbound and outbound IVR (Interactive Voice Response) systems are powerful tools that can help businesses improve efficiency, increase scalability, reduce costs, and improve customer service. Inbound IVR systems handle incoming calls, while outbound IVR systems initiate calls.
When designing an inbound and outbound IVR system, it is important to keep it simple and easy to navigate, provide multiple options, personalize the experience, and provide a way for customers to reach a live agent. Measuring the success of an IVR system is crucial to ensure that it is meeting the needs of customers and achieving desired business outcomes.
Key metrics that can be used to measure the success of an inbound and outbound IVR system include First Call Resolution, Abandonment Rate, Average Handle Time, Customer Satisfaction, Call Volume, and Self Service Success Rate.
By monitoring these metrics, businesses can gain insights into the performance of their IVR system and make adjustments as needed to improve the customer experience and achieve desired business outcomes.
